SAT Math - Geometry Review
Click the link immediately below to view the SAT Verbal diagnostic test.
Verbal
Test
GEOMETRY
Following are some of the basic properties of geometry. You probably know many of them. Memorize any that you do not know.
1. There are 180 degrees in a straight angle.
2. Two angles are supplementary if their angle sum is 180 degrees.
3. Two angles are complementary if their angle sum is 90 degrees.
4. Perpendicular lines meet at right angles.
5. A triangle with two equal sides is called isosceles. The angles opposite the equal sides are called the base angles.
6. The altitude to the base of an isosceles or equilateral triangle bisects the base and bisects the vertex angle.
7. The angle sum of a triangle is 180 degrees.
8. In an equilateral triangle all three sides are equal, and each angle is 60 degrees.
9. The area of a triangle is bh/2, where b is the base and h is the height.
10. In a triangle, the longer side is opposite the larger angle, and vice versa.
11. Two triangles are similar (same shape and usually different size) if their corresponding angles are equal. If two triangles are similar, their corresponding sides are proportional.
12. Two triangles are congruent (identical) if they have the same size and shape.
13. In a triangle, an exterior angle is equal to the sum of its remote interior angles and is therefore greater than either of them.
14. Opposite sides of a parallelogram are both parallel and congruent.
15. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
16. If w is the width and l is the length of a rectangle, then its area is A = lw and its perimeter is P 2w + 2l.
17. The volume of a rectangular solid (a box) is the product of the length, width, and height. The surface area is the sum of the area of the six faces.
18. If the length, width, and height of a rectangular solid (a box) are the same, it is a cube. Its volume is the cube of one of its sides, and its surface area is the sum of the areas of the six faces.
19. A tangent line to a circle intersects the circle at only one point. The radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent line at the point of tangency.
20. An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle.
| Example: In the figure to the right, what
is the value of x?
(A) 30 (B) 32 (C) 35 (D) 40 (E) 47 |
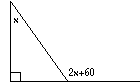 |
Since 2x + 60 is an exterior angle, it is equal to the sum of the remote interior angles.
That is, 2x + 60 = x + 90. Solving for x gives x = 30. The answer is (A).
Most geometry problems on the SAT require straightforward calculations. However, some problems measure your insight into the basic rules of geometry. For this type of problem, you should step back and take a "birds-eye" view of the problem. The following example will illustrate.
| Example: In the figure to the right, O is
both the center of the circle with radius 2 and a vertex of the square OPRS. What is the length
of diagonal PS?
(A) 1/2 (B) 1 (C) 4 (D) 2 (E) 2/3 |
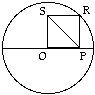 |
The diagonals of a square are equal. Hence, line segment OR (not shown) is equal to SP. Now, OR is a radius of the circle and therefore OR = 2. Hence, SP = 2 as well, and the answer is (D).
|

